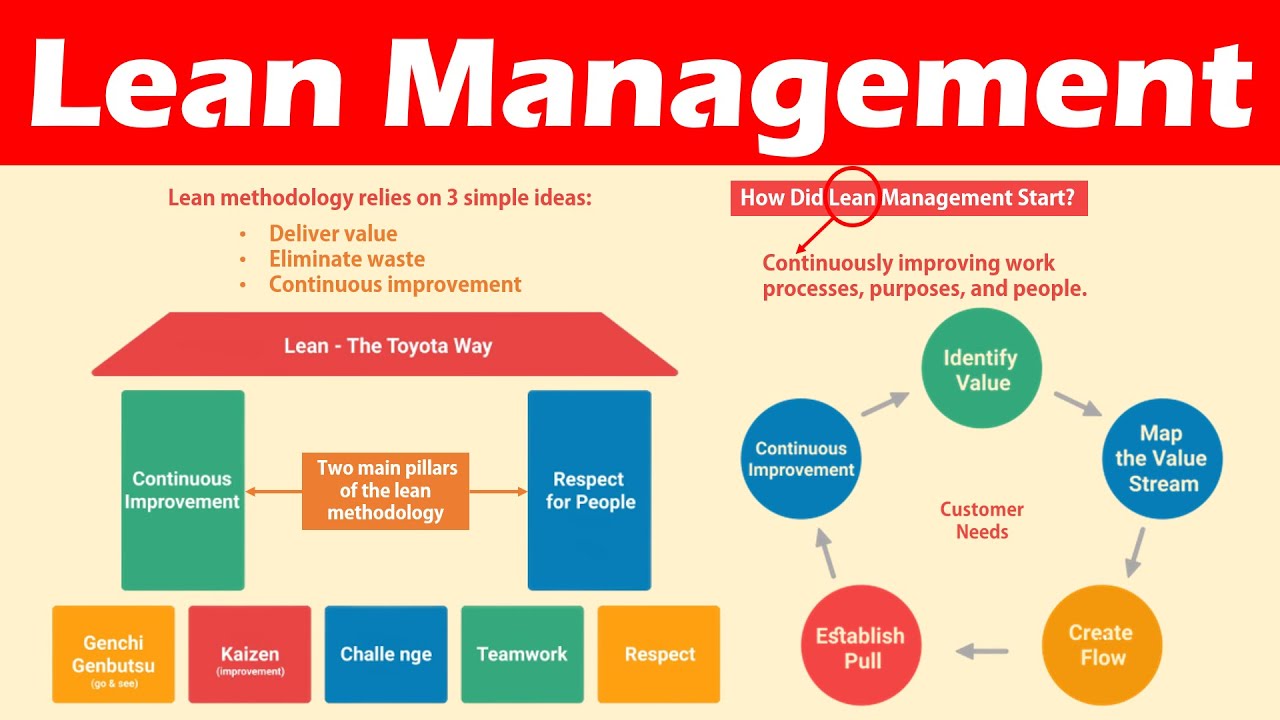
SCOR, a model of process reference developed by Supply Chain Council is widely adopted in industry. It helps companies understand their operational performance, goals and business processes. It allows companies to identify areas of improvement, and compare their performance against that of their competitors.
The model has three main segments: Process modeling, Performance Measurements and Supply Chain Best Practices. The first segment of the model is process modeling, which focuses on planning, sourcing, making and delivering goods. Also included are market interactions, product return management and interaction with customers.
This section also includes over 150 key performance indicator (KPI) metrics that you can utilize to measure your success. As an example, you could evaluate the delivery performance from your suppliers to determine if they deliver quality products for a reasonable rate.
You can also analyze customer returns to determine the savings you would achieve if suppliers reduced their return rates by 20%. This helps you identify areas where you might be able to save money by improving your processes.
The SCOR model can be confusing to those who are unfamiliar with it. The main objective of the model is to create a standard, effective system for managing your supply chains.
It divides the supply chains into ideal business processes. These processes are then divided into categories according to what each process does for your company. It is easy to compare different supply chain activities in your company as well as across industries.
The second segment is the performance measurement, which includes metrics you can use to assess the overall success your supply chain operation. These metrics may be used for evaluations in a number of areas, such as inventory control, transportation costs and supplier quality.
Using performance measurement data, you can find out where your company stands in these areas and create action items to improve the operations. It is important to note that these measures are only useful if you take the time to do something about them.
The first thing you need to do is make a list of KPIs, which you can track. You can review each metric monthly to find out how your business is doing.

It is time to think about new business processes your company could implement that would help improve its operation and increase profits. You can then compare these new processes with those in your existing operations to make sure that they are effective.
This is the perfect way to get your entire team started on improving your company's operations. SCOR is a great way to get your team started on the path of improving supply chain operations.
FAQ
Why automate your warehouse?
Automation has become increasingly important in modern warehousing. E-commerce has brought increased demand for more efficient and quicker delivery times.
Warehouses have to be flexible to meet changing requirements. To do so, they must invest heavily in technology. Automating warehouses has many benefits. Here are some of the reasons automation is worth your investment:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Increases accuracy
-
Safety is boosted
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale up more easily
-
This makes workers more productive
-
Gives you visibility into all that is happening in your warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
It reduces downtime, and increases uptime
-
Quality products delivered on time
-
Eliminates human error
-
Assure compliance with regulations
Can some manufacturing processes be automated?
Yes! Yes. Automation has been around since ancient time. The Egyptians discovered the wheel thousands and years ago. Nowadays, we use robots for assembly lines.
Robotics is used in many manufacturing processes today. They include:
-
Assembly line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots create products
Automation can be applied to manufacturing in many other ways. 3D printing, for example, allows us to create custom products without waiting for them to be made.
What is the importance of automation in manufacturing?
Not only are service providers and manufacturers important, but so is automation. It allows them to offer services faster and more efficiently. It reduces human errors and improves productivity, which in turn helps them lower their costs.
What does warehouse refer to?
A warehouse or storage facility is where goods are stored before they are sold. It can be an indoor space or an outdoor area. Sometimes, it can be both an indoor and outdoor space.
Is there anything we should know about Manufacturing Processes prior to learning about Logistics.
No. No. However, knowing about manufacturing processes will definitely give you a better understanding of how logistics works.
How can we increase manufacturing efficiency?
First, identify the factors that affect production time. We then need to figure out how to improve these variables. If you aren't sure where to begin, think about the factors that have the greatest impact on production time. Once you've identified them, try to find solutions for each of those factors.
Why is logistics important in manufacturing?
Logistics are an essential component of any business. Logistics can help you achieve amazing results by helping to manage product flow from raw materials to finished products.
Logistics play an important role in reducing costs as well as increasing efficiency.
Statistics
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just In Time Method in Production
Just-in time (JIT), is a process that reduces costs and increases efficiency in business operations. It is a process where you get the right amount of resources at the right moment when they are needed. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. He saw how overtime was paid to workers for work that was delayed. He decided to ensure workers have enough time to do their jobs before starting work to improve productivity.
JIT is about planning ahead. You should have all the necessary resources ready to go so that you don’t waste money. Also, you should look at the whole project from start-to-finish and make sure you have the resources necessary to address any issues. You will have the resources and people to solve any problems you anticipate. This will ensure that you don't spend more money on things that aren't necessary.
There are many types of JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This JIT is where you place regular orders for the parts/materials that are needed for your project. This will enable you to keep track of how much material is left after you use it. It will also allow you to predict how long it takes to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This type allows you to stock the materials needed for your projects ahead of time. This allows for you to anticipate how much you can sell.
-
Project-driven: This method allows you to set aside enough funds for your project. Once you have an idea of how much material you will need, you can purchase the necessary materials.
-
Resource-based JIT: This is the most popular form of JIT. You allocate resources based on the demand. You might assign more people to help with orders if there are many. If you don’t have many orders you will assign less people to the work.
-
Cost-based: This is similar to resource-based, except that here you're not just concerned about how many people you have but how much each person costs.
-
Price-based: This is similar to cost-based but instead of looking at individual workers' salaries, you look at the total company price.
-
Material-based: This approach is similar to cost-based. However, instead of looking at the total cost for the company, you look at how much you spend on average on raw materials.
-
Time-based JIT: A variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on how much each employee costs, you focus on how long it takes to complete the project.
-
Quality-based JIT: This is another variation of resource based JIT. Instead of thinking about the cost of each employee or the time it takes to produce something, you focus on how good your product quality.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. In this instance, you are not concerned about the product's performance or meeting customer expectations. Instead, you're focused on how much value you add to the market.
-
Stock-based: This stock-based method focuses on the actual quantity of products being made at any given time. It's useful when you want maximum production and minimal inventory.
-
Just-in-time planning (JIT): This is a combination JIT and supply-chain management. It's the process of scheduling delivery of components immediately after they are ordered. It's important as it reduces leadtimes and increases throughput.