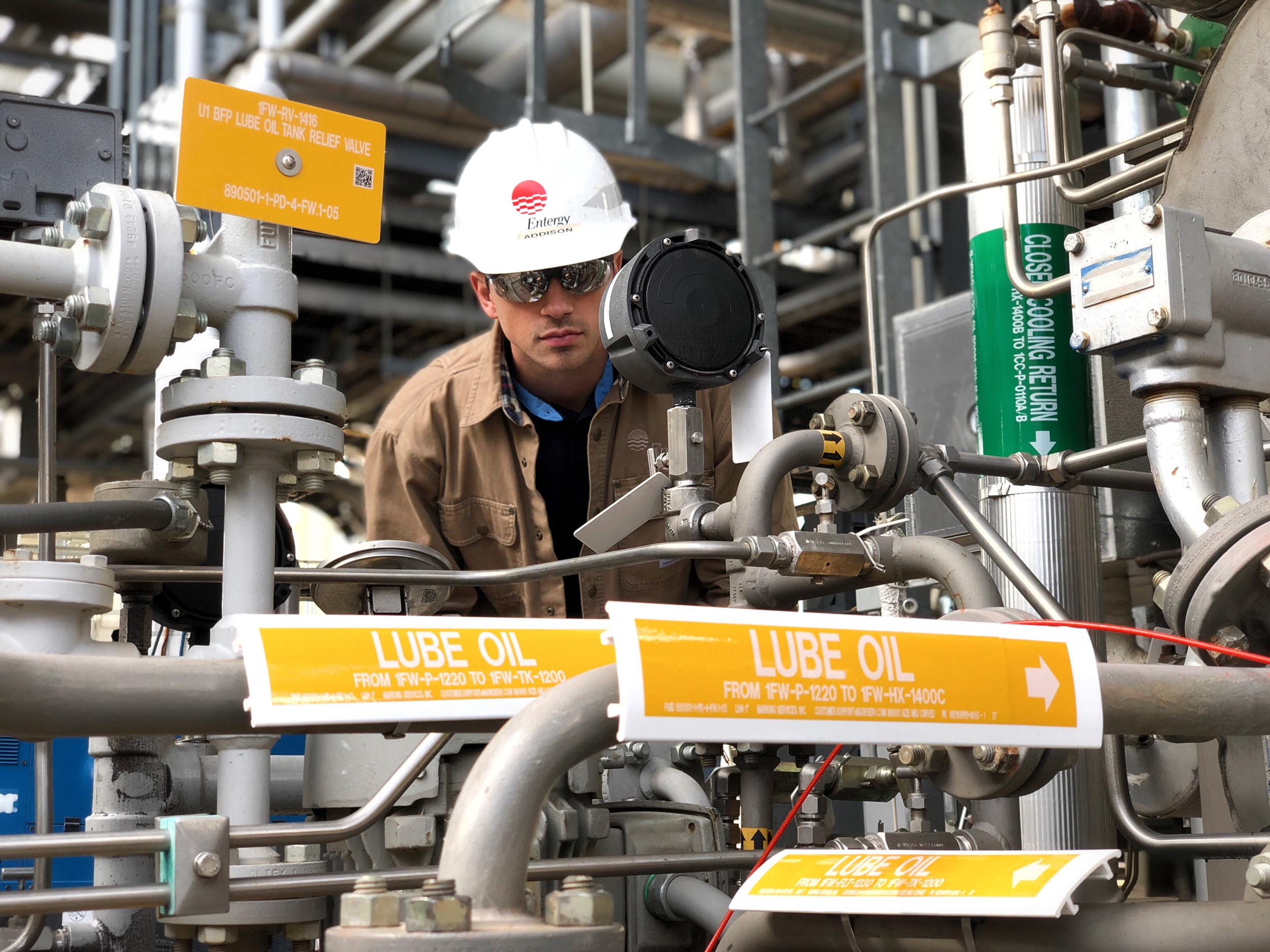

Manufacturing of wind turbines is a job opportunity
The manufacturing of wind turbines requires specialized skills and knowledge. These jobs may include blade epoxies, gears, and tower assembly. A few wind turbine manufacturing firms also have third-party suppliers who can manufacture different components. Wind turbine parts are very large and require to be transported quickly. This task is made possible by teams of rail freight drivers and logisticians.
Most jobs in the manufacturing of wind turbines require a bachelor's or master's degree. Most jobs in the wind turbine industry require engineering or environmental engineering concentrations. Entry-level engineers will need advanced computer skills and experience, in addition to a degree. They often work with more experienced employees to ensure quality and accuracy. They might also be responsible for more complicated projects.
Wind turbine manufacturing processes
The main components of a turbine's wind turbine are the blades. Each blade has two faces connected by integral shear Webs. The blades have a box spar and shell fairings to support them. These structures can withstand edgewise as well as flapwise loads. The spar resists edgewise bends caused by wind pressure or gravitational forces. The blades are shaped to withstand these forces.

The blades can be made of a variety materials. For commercial wind turbine blades, fiberglass is the most widely used material. However, aluminum and lightweight woodens can also be used. The blades are then wrapped in foil and attached to tubes that pump resin.
Competitors within the wind turbine manufacturing sector
While Chinese manufacturers are a growing force in the global wind industry, they are not yet the dominant player. Chinese turbine producers have had trouble eclipsing the incumbent manufacturers in developed countries. They may be able to grow their overseas activities if it is possible to invest in local manufacturing.
Many are opting to build their components themselves, even though large turbine companies are outsourcing increasingly many parts. Both have their advantages and drawbacks. Vestas in Pueblo (Colorado) has adopted this strategy and now manufactures wind turbine towers to support third-party US projects. The agreement allows the tower plant up to 25% of its production capacity, and provides 100 jobs. But, this approach comes with a drawback: weak quality control. There have been instances in the past when components that were outsourced failed, such as gearbox failures and blade cracking. Some foundations built offshore even contain low-quality steel.
Safety and health concerns regarding wind turbine manufacturing
In wind turbine manufacturing, safety and health is an important concern. The hazards faced by workers can result in long-term injuries or even fatalities. There are several ways to reduce the risk. These include proper training and routine inspections. Here are some tips to help employees stay safe working in wind turbine manufacturing facilities.
One of the most common hazards in wind turbine blade manufacturing is the exposure to harmful gases, vapors, and dust. To reduce this risk, workers must wear respirators. They also need to be trained on how to use them. It is important to have ear protection and good training.
FAQ
What is the difference between manufacturing and logistics
Manufacturing is the production of goods using raw materials. Logistics manages all aspects of the supply chain, including procurement, production planning and distribution, inventory control, transportation, customer service, and transport. Manufacturing and logistics can often be grouped together to describe a larger term that covers both the creation of products, and the delivery of them to customers.
Is there anything we should know about Manufacturing Processes prior to learning about Logistics.
No. No. Knowing about manufacturing processes will help you understand how logistics works.
What does it mean to warehouse?
A warehouse or storage facility is where goods are stored before they are sold. It can be either an indoor or outdoor space. In some cases it could be both indoors and outdoors.
How does a production planner differ from a project manager?
A production planner is more involved in the planning phase of the project than a project manger.
What are the essential elements of running a logistics firm?
You need to have a lot of knowledge and skills to manage a successful logistic business. Effective communication skills are necessary to work with suppliers and clients. You must be able analyze data and draw out conclusions. You must be able to work well under pressure and handle stressful situations. You must be creative and innovative to develop new ideas to improve efficiency. You must be a strong leader to motivate others and direct them to achieve organizational goals.
You must be organized to meet tight deadlines.
Statistics
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma: How to Use it in Manufacturing
Six Sigma is defined as "the application of statistical process control (SPC) techniques to achieve continuous improvement." It was developed by Motorola's Quality Improvement Department at their plant in Tokyo, Japan, in 1986. The basic idea behind Six Sigma is to improve quality by improving processes through standardization and eliminating defects. Since there are no perfect products, or services, this approach has been adopted by many companies over the years. Six Sigma's primary goal is to reduce variation from the average value of production. It is possible to measure the performance of your product against an average and find the percentage of time that it differs from the norm. If this deviation is too big, you know something needs fixing.
Understanding the nature of variability in your business is the first step to Six Sigma. Once you have a good understanding of the basics, you can identify potential sources of variation. Also, you will need to identify the sources of variation. Random variations occur when people make mistakes; systematic ones are caused by factors outside the process itself. If you make widgets and some of them end up on the assembly line, then those are considered random variations. It would be considered a systematic problem if every widget that you build falls apart at the same location each time.
Once you identify the problem areas, it is time to create solutions. That solution might involve changing the way you do things or redesigning the process altogether. To verify that the changes have worked, you need to test them again. If they didn't work, then you'll need to go back to the drawing board and come up with another plan.