
It is hard to choose which articles are most commonly cited, considering the numerous articles that have been published on supply-chain management. Given the amount of academic research on this topic, it is hard to answer. However, one can narrow down the field using cocitation analysis. Using the cocitation of the Supply Chain Management Association's database, we uncovered the most cited supply chain related articles, with the International Journal of Supply Chain Management leading the pack with a whopping 25,476 citations. According to the most-cited article, the citations are divided into five categories. Because the International Journal of Supply Chain Management has an extremely high citation count, the order of the citations can be unpredictable.
A review of Amazon's supply chain practices, which links buyers and sellers, is the most popular article. It was also the most accurate reflection of the research. This review will reveal what works and what does not. The article describes the pitfalls and opportunities Amazon faces and suggests some solutions.
Cross-sectional studies of supply chain risk and performance are the most popular. The study uses both panel and regression data to evaluate the effects of supply-related risks on performance. This is no easy task. The results are amazing. Particularly, the study shows that supply-chain risk management is the best option to improve long-term performance. This also has implications for other areas in corporate life such as procurement or customer service.
The most cited article is not the only notable feat of the same caliber. It is not surprising that the journal with the highest citations has the most publications in the Supply Chain Management Association's database. The International Journal of Supply Chain Management, which is the Supply Chain Management Association’s flagship journal has the highest citation count with 25,476 references. This is almost twice as many as the International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, which is the sister journal of Supply Chain Management Association.
FAQ
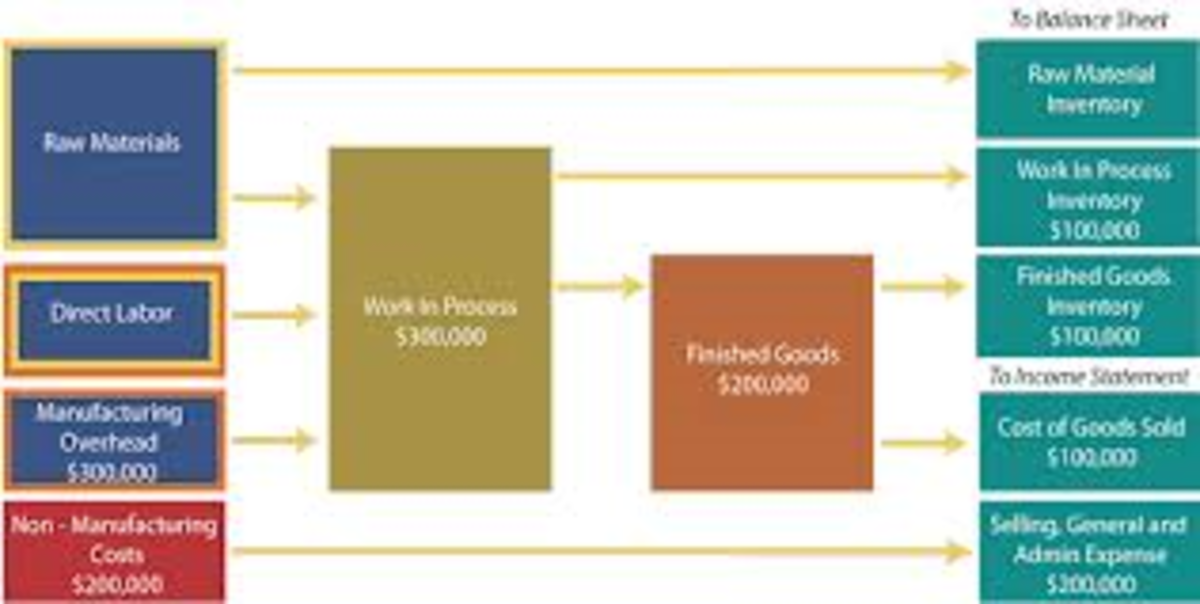
What are the four types of manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process by which raw materials are transformed into useful products through machines and processes. It can involve many activities like designing, manufacturing, testing packaging, shipping, selling and servicing.
How can we reduce manufacturing overproduction?
Improved inventory management is the key to reducing overproduction. This would decrease the time that is spent on inefficient activities like purchasing, storing, or maintaining excess stock. We could use these resources to do other productive tasks.
You can do this by adopting a Kanban method. A Kanban board, a visual display to show the progress of work, is called a Kanban board. Kanban systems allow work items to move through different states until they reach their final destination. Each state represents a different priority.
For instance, when work moves from one stage to another, the current task is complete enough to be moved to the next stage. A task that is still in the initial stages of a process will be considered complete until it moves on to the next stage.
This helps to keep work moving forward while ensuring that no work is left behind. Managers can see how much work has been done and the status of each task at any time with a Kanban Board. This allows them the ability to adjust their workflow using real-time data.
Lean manufacturing is another way to manage inventory levels. Lean manufacturing seeks to eliminate waste from every step of the production cycle. Waste includes anything that does not add value to the product. There are several types of waste that you might encounter:
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Exceed materials
These ideas will help manufacturers increase efficiency and lower costs.
What are the responsibilities for a manufacturing manager
The manufacturing manager should ensure that every manufacturing process is efficient and effective. They should be alert for any potential problems in the company and react accordingly.
They should also learn how to communicate effectively with other departments, including sales and marketing.
They should also be aware of the latest trends in their industry and be able to use this information to help improve productivity and efficiency.
What are the requirements to start a logistics business?
It takes a lot of skills and knowledge to run a successful logistics business. Good communication skills are essential to effectively communicate with your suppliers and clients. You should be able analyse data and draw inferences. You must be able and able to handle stress situations and work under pressure. To improve efficiency, you must be innovative and creative. You need to have strong leadership qualities to motivate team members and direct them towards achieving organizational goals.
You should also be organized and efficient to meet tight deadlines.
Are there any Manufacturing Processes that we should know before we can learn about Logistics?
No. No. But, being familiar with manufacturing processes will give you a better understanding about how logistics works.
Statistics
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use Lean Manufacturing in the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing refers to a method of managing that seeks to improve efficiency and decrease waste. It was developed in Japan during the 1970s and 1980s by Taiichi Ohno, who received the Toyota Production System (TPS) award from TPS founder Kanji Toyoda. Michael L. Watkins published the "The Machine That Changed the World", the first book about lean manufacturing. It was published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes the elimination and minimization of waste in the value stream. Lean manufacturing is called just-in-time (JIT), zero defect, total productive maintenance (TPM), or 5S. Lean manufacturing eliminates non-value-added tasks like inspection, rework, waiting.
Lean manufacturing improves product quality and costs. It also helps companies reach their goals quicker and decreases employee turnover. Lean manufacturing has been deemed one of the best ways to manage the entire value-chain, including customers, distributors as well retailers and employees. Many industries worldwide use lean manufacturing. Toyota's philosophy is a great example of this. It has helped to create success in automobiles as well electronics, appliances and healthcare.
Five fundamental principles underlie lean manufacturing.
-
Define Value - Identify the value your business adds to society and what makes you different from competitors.
-
Reduce Waste – Eliminate all activities that don't add value throughout the supply chain.
-
Create Flow – Ensure that work flows smoothly throughout the process.
-
Standardize and simplify - Make your processes as consistent as possible.
-
Build Relationships- Develop personal relationships with both internal as well as external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing is not a new concept, but it has been gaining popularity over the last few years due to a renewed interest in the economy following the global financial crisis of 2008. Many companies have adopted lean manufacturing methods to increase their marketability. Many economists believe lean manufacturing will play a major role in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These include improved customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels, lower operating costs, increased productivity, and better overall safety.
The principles of lean manufacturing can be applied in almost any area of an organization. However, it is particularly useful when applied to the production side of an organization because it ensures that all steps in the value chain are efficient and effective.
There are three types of lean manufacturing.
-
Just-in-Time Manufacturing: Also known as "pull systems", this type of lean manufacturing uses just-in-time manufacturing (JIT). JIT is a process in which components can be assembled at the point they are needed, instead of being made ahead of time. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing: ZDM ensures that no defective units leave the manufacturing plant. If a part needs to be fixed during the assembly line, it should be repaired rather than scrapped. This applies to finished goods that may require minor repairs before shipment.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous improvement refers to continuous improvement of processes as well people and tools.