
Industrial engineers need to have strong math skills and a background in physical sciences. They also need to be able to solve problems. They can work in many sectors such as manufacturing, construction and health care. They can work in the office or on the floor of the factory.
Industrial engineers analyse production processes, design manufacturing techniques, improve efficiency, and make decisions about how to improve them. They also help to develop quality control processes. They can also establish manufacturing standards or train staff. Individuals who are interested to become industrial engineers must be willing and able to collaborate with others. They should be driven to improve efficiency and streamline their processes. They should possess excellent leadership and communication skills and be adept at solving problems.
Industrial engineers can create cost analysis tools and help robots run more efficiently. They also use data analysis to determine if processes have been optimized. They may also develop manufacturing standards and design standards, and they will be responsible for ensuring that processes meet safety standards. They will also be responsible for creating documentation and developing procedures for equipment control and inventory tracking. They might present their plans in written reports or oral presentations.
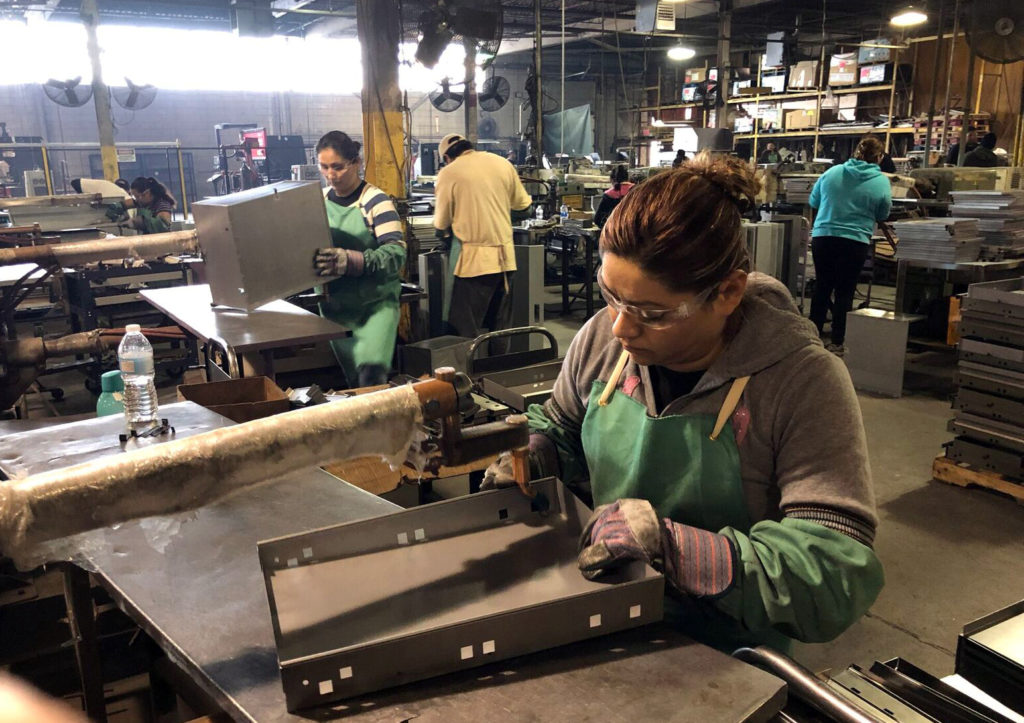
Industrial engineers can work in factories, offices, or warehouses. They may also travel to their clients' sites. They may need to work in noisy or cramped spaces. They may need to wear protective safety clothes. Sometimes they will need to work more than normal in order to meet production deadlines.
Industrial engineers are responsible for designing and implementing processes, ensuring that they operate efficiently and that the products are of high quality. They can also help solve production problems. Some industrial engineers can also start manufacturing businesses. They may have to train new workers and make sure that they know how to do their jobs properly. They may also have the responsibility of ensuring that raw materials meet certain quality standards before they can be used in manufacturing.
Industrial engineers work with other departments to create integrated systems for managing industrial production processes. They may specialize in one area of engineering. They may have to work in a cramped or noisy environment, and they may have to work overtime to address unexpected problems in manufacturing. They may need to travel to warehouses or construction sites to gather data, and they may have to work with other professionals to find solutions to manufacturing problems.
Industrial engineers can advance through education or experience, and they may move to management positions. They could also set up their own consulting businesses or become specialists in a certain area. They may be specialists in quality control, facility planning, or other areas. They may also be responsible designing production layouts. They could also be responsible in developing wage and pay administration systems. They may also be responsible scheduling deliveries based in production forecasts, storage, handling, and maintenance requirements. They might also be required to travel to other locations and carry out administrative tasks. They might also supervise technicians.

An industrial engineer may work for a company, or as a consultant. They may work a standard 40-hour work week or more, depending on the company's needs. They may also work more than 40 hours in a consulting service if they are providing technical support for a business.
FAQ
What are the main products of logistics?
Logistics is the process of moving goods from one point to another.
They cover all aspects of transportation, such as packing, loading, transporting and unloading.
Logisticians ensure that the right product reaches the right place at the right time and under safe conditions. Logisticians help companies improve their supply chain efficiency by providing information about demand forecasts and stock levels, production schedules, as well as availability of raw materials.
They can also track shipments in transit and monitor quality standards.
How can excess manufacturing production be reduced?
Improved inventory management is the key to reducing overproduction. This would reduce the amount of time spent on unnecessary activities such as purchasing, storing, and maintaining excess stock. This would allow us to use our resources for more productive tasks.
A Kanban system is one way to achieve this. A Kanban Board is a visual display that tracks work progress. Kanban systems allow work items to move through different states until they reach their final destination. Each state has a different priority level.
For instance, when work moves from one stage to another, the current task is complete enough to be moved to the next stage. It is possible to keep a task in the beginning stages until it gets to the end.
This allows work to move forward and ensures that no work is missed. Managers can see how much work has been done and the status of each task at any time with a Kanban Board. This information allows managers to adjust their workflow based off real-time data.
Lean manufacturing, another method to control inventory levels, is also an option. Lean manufacturing works to eliminate waste throughout every stage of the production chain. Waste includes anything that does not add value to the product. Some common types of waste include:
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Materials in excess
Manufacturers can increase efficiency and decrease costs by implementing these ideas.
How does a Production Planner differ from a Project Manager?
The main difference between a production planner and a project manager is that a project manager is usually the person who plans and organizes the entire project, whereas a production planner is mainly involved in the planning stage of the project.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
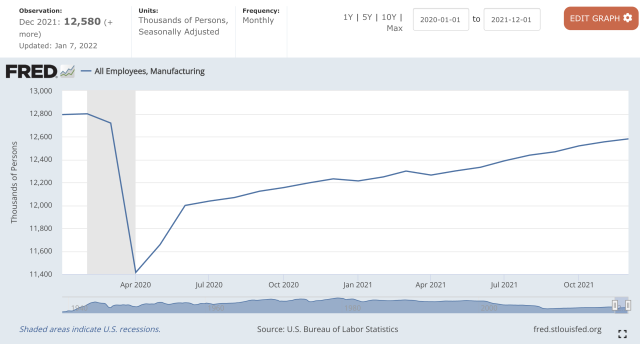
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use 5S to Increase Productivity in Manufacturing
5S stands in for "Sort", the "Set In Order", "Standardize", or "Separate". Toyota Motor Corporation invented the 5S strategy in 1954. It improves the work environment and helps companies to achieve greater efficiency.
The idea behind standardizing production processes is to make them repeatable and measurable. This means that tasks such as cleaning, sorting, storing, packing, and labeling are performed daily. Because workers know what they can expect, this helps them perform their jobs more efficiently.
Implementing 5S requires five steps. These are Sort, Set In Order, Standardize. Separate. And Store. Each step requires a different action, which increases efficiency. For example, when you sort things, you make them easy to find later. When you set items in an order, you put items together. Next, organize your inventory into categories and store them in containers that are easily accessible. Labeling your containers will ensure that everything is correctly labeled.
This requires employees to critically evaluate how they work. Employees need to understand the reasons they do certain jobs and determine if there is a better way. They will need to develop new skills and techniques in order for the 5S system to be implemented.
In addition to increasing efficiency, the 5S method also improves morale and teamwork among employees. They feel more motivated to work towards achieving greater efficiency as they see the results.