Lean manufacturing has many benefits, but companies still face challenges when implementing it. Companies need to develop a comprehensive plan for overcoming these obstacles. Companies that have implemented Lean have found that there are three main issues that are responsible for limiting the success of the initiative.
No matter how large a company is, lean manufacturing commitments are crucial to their success. Although there is no way to know how committed a company to lean manufacturing, it is essential that they educate their employees on the new corporate culture.
Also important is to ensure that resources have been allocated properly. Many public organizations have found that they are wasting allocated budgets on items that are not necessary. Reports also indicate that some managers purchase equipment that isn't necessary to make use of the budget. This can cause operational bottlenecks that lead to inefficient lean manufacturing.
Resistance to cultural changes is one of the biggest obstacles in lean manufacturing. Many employees, especially those who have been in the company for a long period, aren't comfortable with changes. Some of these employees may wait for the voice of the majority to sway them into the new direction. Management must communicate the advantages of the program and the reasons for the change in order to break the resistance.
Another significant challenge is the lack of a strategic transformation plan. Even though many companies transform their business operations simultaneously, it is important that you have a long-term plan. This strategy allows companies identify and mentor future leaders, keep them competitive and improve operations. It helps identify operational bottlenecks and addresses growth opportunities.
To overcome resistance, it is important to have training. Correct training helps workers to understand their responsibilities. This training helps workers acquire multi skills that can be used to help them work independently. Additionally, training helps workers improve their problem solving skills which will help them to sustain Lean through improved performance.
To overcome resistance, management needs to engage with workers frequently. Managers may try to force workers to follow their instructions but they must also explain why it is necessary. In some instances, managers were found to have given incorrect instructions to their workers, which resulted in ineffective implementation.
Managers must participate on the shop floor regardless of their company's size. This allows them to spot areas that need improvement. They also need to develop structured training modules and acquaint staff with the introduction of new digital work tools. These tools such as 5S improve visual management.
It is crucial to communicate and develop a clear vision of how lean manufacturing will be implemented. This vision should outline the responsibilities of employees and include a schedule to implement lean. It also includes a method for measuring success.
FAQ
How can I find out more about manufacturing?
The best way to learn about manufacturing is through hands-on experience. But if that is not possible you can always read books and watch educational videos.
What kind of jobs are there in logistics?
There are many kinds of jobs available within logistics. Some examples are:
-
Warehouse workers - They load and unload trucks and pallets.
-
Transportation drivers – These drivers drive trucks and wagons to transport goods and pick up the goods.
-
Freight handlers - They sort and pack freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers – These people oversee inventory at warehouses.
-
Sales representatives - They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators – They plan and coordinate logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents: They are responsible for purchasing goods and services to support company operations.
-
Customer service representatives – They answer emails and phone calls from customers.
-
Shipping clerks - They process shipping orders and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - They fill orders based on what is ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors: They inspect outgoing and incoming products for any defects.
-
Other - Logistics has many other job opportunities, including transportation supervisors, logistics specialists, and cargo specialists.
What is the difference in Production Planning and Scheduling, you ask?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. This is accomplished by forecasting the demand and identifying production resources.
Scheduling refers the process by which tasks are assigned dates so that they can all be completed within the given timeframe.
What is the role of a production manager?
Production planners ensure all aspects of the project are delivered within time and budget. They also ensure that the product/service meets the client’s needs.
Statistics
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
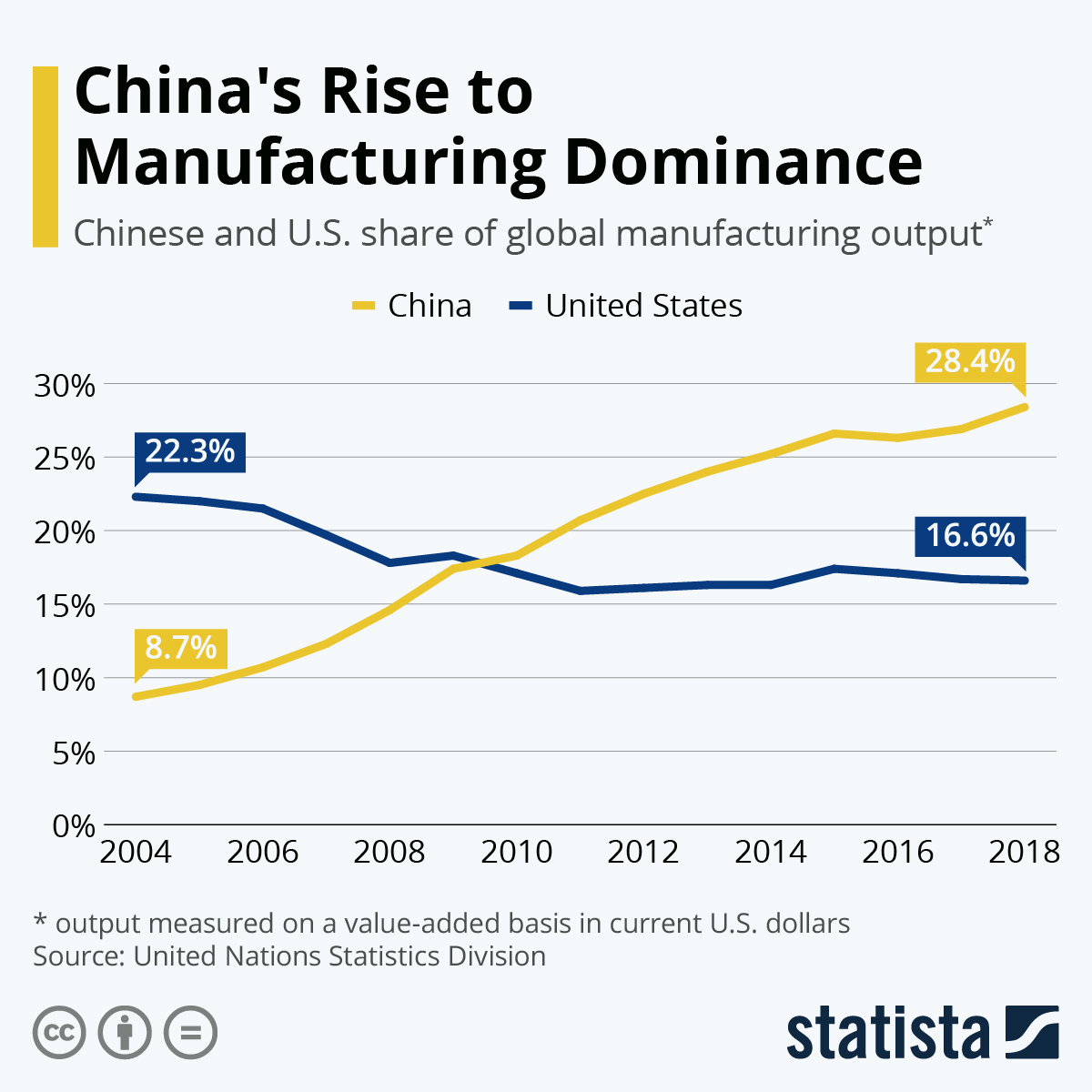
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to use the Just-In Time Method in Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It is a process where you get the right amount of resources at the right moment when they are needed. This means that only what you use is charged to your account. Frederick Taylor was the first to coin this term. He developed it while working as a foreman during the early 1900s. He noticed that workers were often paid overtime when they had to work late. He concluded that if workers were given enough time before they start work, productivity would increase.
JIT is about planning ahead. You should have all the necessary resources ready to go so that you don’t waste money. You should also look at the entire project from start to finish and make sure that you have sufficient resources available to deal with any problems that arise during the course of your project. You'll be prepared to handle any potential problems if you know in advance. This will ensure that you don't spend more money on things that aren't necessary.
There are many types of JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This JIT is where you place regular orders for the parts/materials that are needed for your project. This will allow to track how much material has been used up. This will allow you to calculate how long it will take to make more.
-
Inventory-based: This type allows you to stock the materials needed for your projects ahead of time. This allows you predict the amount you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven : This is a method where you make sure that enough money is set aside to pay the project's cost. Knowing how much money you have available will help you purchase the correct amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT: This type of JIT is most commonly used. Here, you allocate certain resources based on demand. For instance, if you have a lot of orders coming in, you'll assign more people to handle them. If you don't have many orders, you'll assign fewer people to handle the workload.
-
Cost-based: This approach is very similar to resource-based. However, you don't just care about the number of people you have; you also need to consider how much each person will cost.
-
Price-based pricing: This is similar in concept to cost-based but instead you look at how much each worker costs, it looks at the overall company's price.
-
Material-based is an alternative to cost-based. Instead of looking at the total cost in the company, this method focuses on the average amount of raw materials that you consume.
-
Time-based: This is another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing solely on the amount each employee costs, focus on how long it takes for the project to be completed.
-
Quality-based JIT - This is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each worker or how long it takes, think about how high quality your product is.
-
Value-based: This is one of the newest forms of JIT. In this scenario, you're not concerned about how products perform or whether customers expect them to meet their expectations. Instead, your focus is on the value you bring to the market.
-
Stock-based. This method is inventory-based and focuses only on the actual production at any given point. This method is useful when you want to increase production while decreasing inventory.
-
Just-in-time planning (JIT): This is a combination JIT and supply-chain management. It refers to the process of scheduling the delivery of components as soon as they are ordered. It is essential because it reduces lead-times and increases throughput.